Jie Zhou
07/28/2011
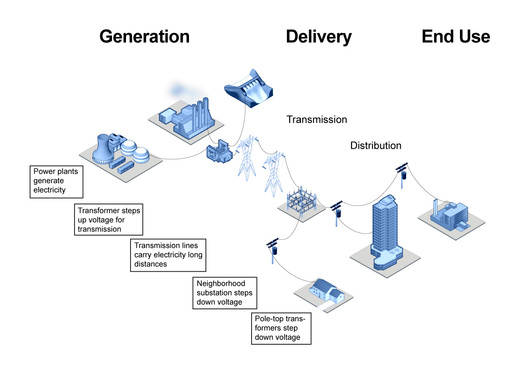
The Traditional Grid
Some problems with the existing grid:
- getting old and worn out
- population growth cause the transmission system overused and gragile
- reliability of the grid decline
Versus the Smart Grid
The most important and distinctive characteristic of the Smart Grid is its "intelligence" and two-way communication capabilities.
Functions
- Self-healing from power disturbance events
Automatically detects and responds to grid problems, ensuring quick recovery after disturbances. The incorporation of microgrids also means that affected areas can be isolated from the main network as to cause minimal disruption to services,
- Enabling active participation by consumers in demand response
The development of the smart grid and associatd smart technologies and devices will allow users to have more direct control over the energy they use on a day-to-day basis. Like changing what they need from a power supplier, moving towards flexible energy, cheaper alternatives and the option for microgeneration
- Variety of generation options
The current electricity grid cannot integrated well of energy being drawn from a variety of energy sources, like solar, wind turbine, etc. but this is the aim of the smart grid
- Providing higher quality power that will save money wasted from outage
Assuring more stable electricity, avoiding outages or blackouts to reduce economic loss
- Accommodating all generation and storage options
All sources will be interconnected allowing consumers to access a general and renewable generated source of energy. Energy that is generated during non-peak timses can be stored for potential usage to ensure minimal wastage.
- Enabling new products, services, and markets
Creating an open market where alternative energy sources can be sold to customers regardless of location. Microgeneration (like some large networks such as offices) can generate own power through solar panels, wind turbines and in turn can supply energy back to the central net work grid, and make some money on it.
- Optimizing assets and operating efficiently
Generate more power through the existing systems by optimizing them, allowing the reduction of power flow waste and maximizing the distribution of lower-costgeneration sources.
Major Driving Forces
Obstables
One-half of the utilities surveyed in the recent Pacific Crest Mosaic Smart Grid Survey named rate Cost as the strongest barrier to Smart Grid projects within their organization. Technology immaturity is also a key barrier to Smart Grid projects but is rated a “top” barrier for fewer respondents.
Regulatory Barriers and Lack of Open Standards are some of the other obstacles.
Smart grids by country
Australia
The Australian government has committed to investing $100 m in smart grids. They said they will build the smart grid over five sites in New South Wales
Canada
The government of Ontario, Canada, through the Energy Conservation Responsibility Act [3] in 2006, has mandated the installation of Smart Meters in all Ontario businesses and households by 2010.
China
As part of its current 5-year plan, China is building a Wide Area Monitoring system (WAMS). On May 21, 2009, China has announced an aggressive framework for Smart Grid deployment.
European Union
Development of smart grid technologies is part of the European Technology Platform (ETP) initiative and is called the SmartGrids Technology platform. The SmartGrids Technology Platform began its work in 2005. Its aim is to formulate and promote a vision for the development of European electricity networks looking towards 2020 and beyond
Republic of Korea
On January 2010, the Korean government has launched a $65 million pilot program consists of several programs, one of which is a fully integrated Smart Grid System for 6000 households
The Korean government seeks to complete the installation of smart grid in the country by 2030 and establish another 27,000 or more power charge stations for electric cars. A total of 27.5 trillion won will be injected according to the roadmap.
United States
Support for smart grids became federal policy with passage of the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007. The law, Title13, sets out $100 million in funding per fiscal year from 2008–2012.
Smart grids received further support with the passage of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, which set aside $11 billion for the creation of a smart grid.
Source: